Drug Resistant Salmonella Infantis Prevalent in U.S.
|
12/01/2020 |
|
According to a recent publication* a Salmonella Infantis clone has emerged that is resistant to beta-lactam and fluroquinolone drugs. The strain carries a beta-lactamase gene, balCTX-M-65 and a gyrA mutation imparting resistance to fluroquinolone.
According to the authors, routine surveillance by the National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System determined that the clone represented 29 percent of all Salmonella isolates from retail chickens and seven percent from retail turkey in 2019. There was a close relationship based on genomic sequence assays among the poultry isolates and those derived from human cases of salmonellosis. The clone has spread rapidly since first identified in 2014 and has the potential to be of clinical significance in human cases of S. Infantis infection.
|
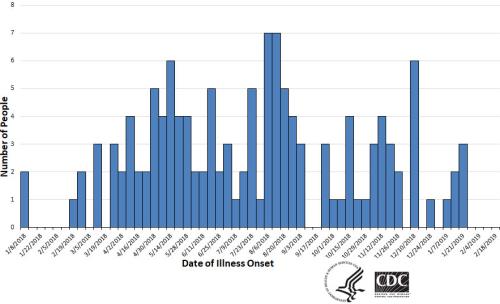
CDC Epicurve for S. Infantis |
|
*Tyson, G. et al A multidrug-resistant Salmonella Infantis clone is spreading and recombining in the United States. Microbial Drug Resistance. doi.org/10.1089/mdr.22.0389 November 24, 2020.
|

|
|
|